Heap Sort
What is a heap?
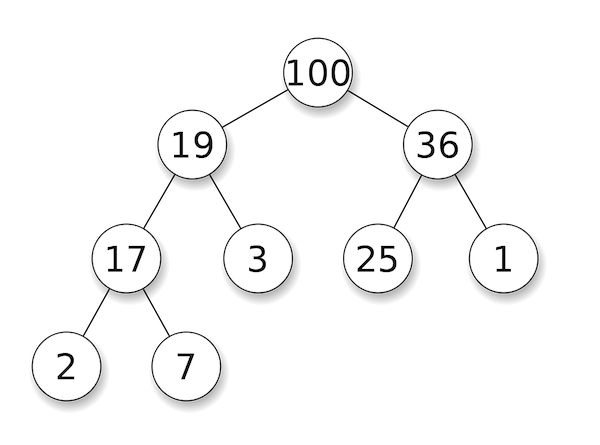
A heap is a tree that has the "heap" property. There can be either max heaps or min heaps. A max heap has the property that for every parent node, it's key is greater than or equal to the key of its child nodes. In other words, in a max heap, the biggest number is at the top.
A min heap is similar to a max heap, except that the parent's key is less than or equal to the child's key. Therefore in a min heap, the smallest number is at the top (or root) of the tree.
What is heapsort?
Heapsort uses a heap data structure in order to perform a sort. It's an in-place comparison sort. The code implementation uses 3 functions: Heapsort, BuildHeap, and Heapify. Heapsort is the main/entry function, BuildHeap forms your initial heap, and Heapify is to make a non-heap tree into a heap. An important thing to recognize is that an array can be a representation of a tree. Imagine arr[0] as the root of the tree and arr[1] and arr[2] as the left and right nodes of the root. Then arr[3] and arr[4] would be the left and right nodes of arr[1], and so on. For example, take the max heap pictured above. In an array representation that would look like:
Thus, for any given index i, its children are:
left:
2*i + 1right:
2*i + 2
Pseudocode
The pseudocode for the algorithm goes like this: 1. Using the given array, build a heap using recursive insertion 2. Iterate to extract the max element in the heap and then reheapify the heap 3. Extracted elements form a sorted subsequence
Code in Python
For working code in Python, visit this repl.
References
Last updated